Bard Unleashed: Google's AI Powerhouse Takes on OpenAI's GPT-4 Supremacy
AI at War
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Google has recently announced the limited public rollout of its new AI chatbot, Bard, aimed at competing with OpenAI's GPT-4 model. Initially available for users in the U.K. and the U.S., those interested can join a waitlist at bard.google.com. Described as an "early experiment that lets you collaborate with generative AI," Bard offers users the ability to ask questions and refine answers through follow-up queries.
Similar to OpenAI's ChatGPT and Microsoft's Bing chatbot, Bard is based on a large language model. Developed using Google's LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications), Bard assists in boosting productivity, accelerating ideas, and fueling curiosity. Users can seek tips to achieve their goals, such as reading more books, requesting explanations of complex concepts like quantum physics in simpler terms, or even seeking creative inspiration for writing a blog post.

Google unveiled Bard last month through a blog post by CEO Sundar Pichai, which highlighted the chatbot's capabilities in handling "NORA" queries or questions that have "no one right answer." However, conversational AI raises concerns about accuracy, information sources, and ethical boundaries.
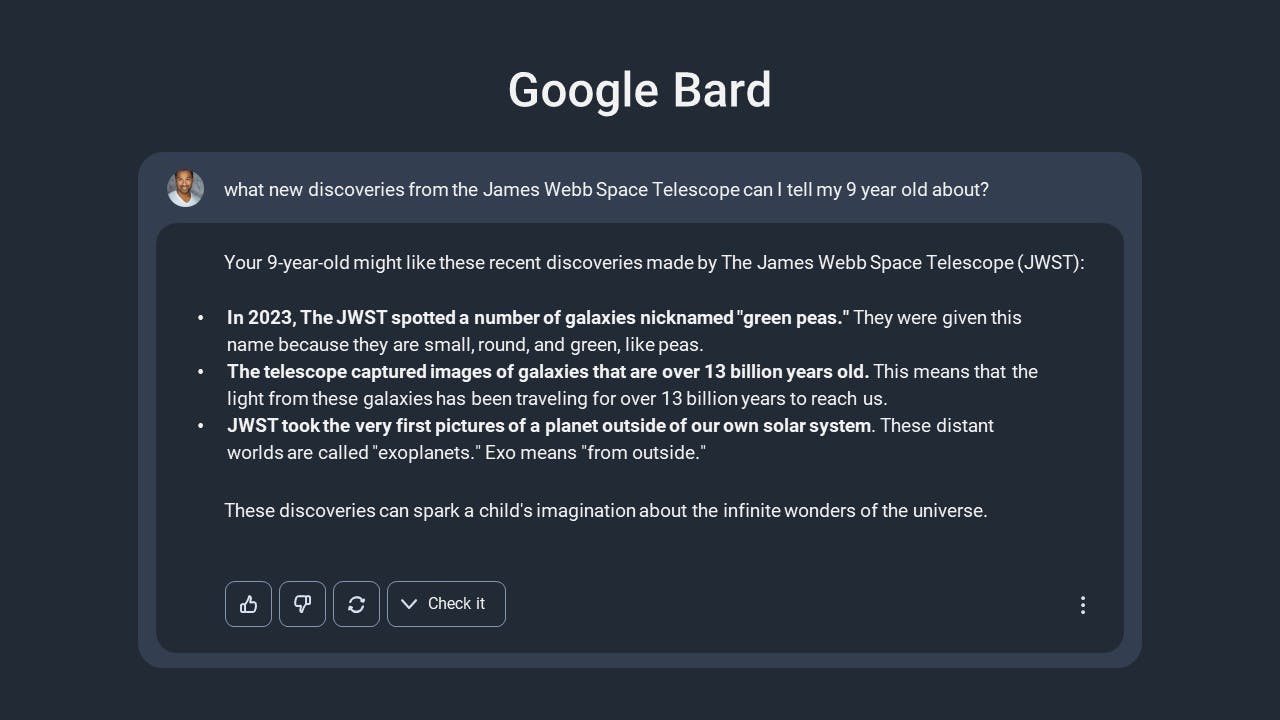
Bard's interface presents users with a blank chatbox accompanied by a disclaimer stating that the AI may display inaccurate or offensive information that doesn't represent Google's views. Users can type any question in the text field and Bard will generate a response. While the answers appear all at once instead of being typed word by word, Google claims that Bard works similarly to other generative AI chatbots, predicting the next word based on previous words.
Users can rate Bard's answers using thumbs up or thumbs down icons, restart the conversation, or click the "Google It" button to switch to Google's search engine. Unlike Microsoft's Bing chatbot, Bard doesn't provide footnotes with web sources, but users can view alternative answers by clicking the "View other drafts" option in the top-right corner.

Currently, Bard operates as a standalone product separate from Google's search engine. As the platform becomes more widely available, it will be interesting to observe user interactions, as well as the reactions of regulators and content creators, particularly concerning potential plagiarism and Google's relationship with third-party websites. The limited release of Bard marks the beginning of a long journey, with many exciting developments expected in the future.
ARE YOU READY?
Let me know your thoughts in the comment section.

